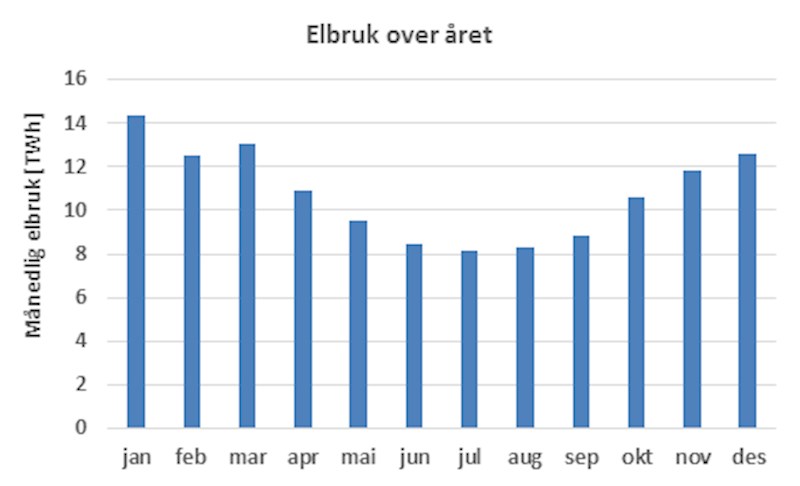
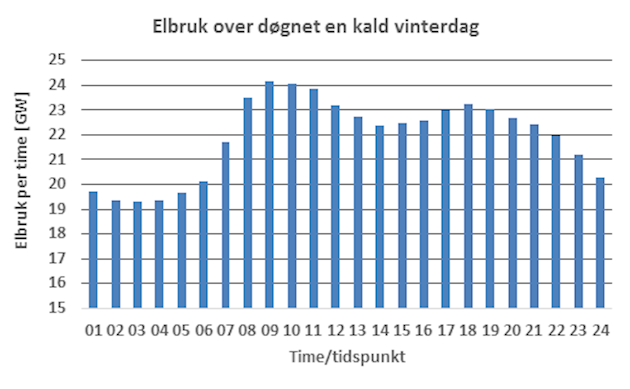
The consumption of electricity varies over the day and the year, depending on the temperature and activity of business and household. Normally, the consumption of electricity is lowest at night and highest in the morning and afternoon. The high proportion of electricity for space heating in households and commercial buildings means that the consumption of electricity is highest in winter. This leads to the tops in the electricity consumption usually occurs in the morning on cold winter days. These traits of electricity consumption are illustrated in the figures below.
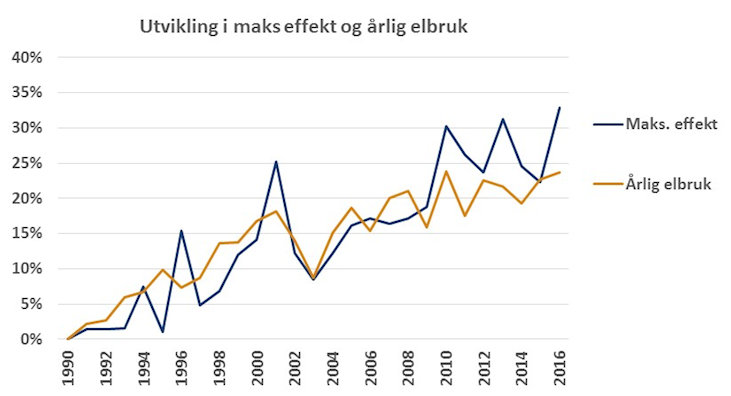
Electricity consumption in a single moment is called power consumption. Since 1990, power consumption has grown faster than annual electricity consumption, as shown in the figure below. This development may come from several power-consuming devices. Previous record of average power consumption over one hour was measured on January 21, 2016 from eight to nine in the morning. During this hour, electricity consumption was 24.49 GWh.
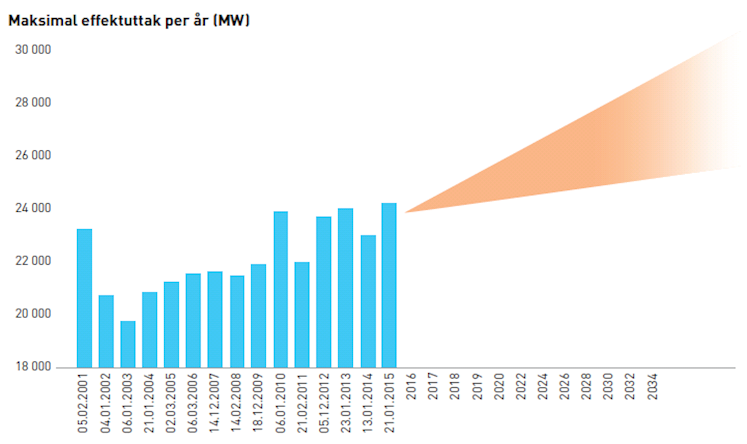
Starting more power-consuming appliances in households and electrification of the transport sector can cause power consumption to continue to grow faster than annual electricity consumption in the future. Better buildings with lower heating requirements and relocation of consumption, such as charging electric cars, at the time of day with lower overall power consumption will dampen such a development. This is beneficial for the power grid, which is dimensioned in relation to power consumption. The figure below illustrates a possible development in maximum power output and shows that it is highly uncertain about future Developments.